Let’s talk about inflammation.
Many have deemed inflammation the driver of all chronic diseases – but, inflammation is crucial to our survival and bodily protection. We need inflammation to heal.
So, what is the balance? And how can we find it?
This blog covers all of that and more – keep reading for all things inflammation.
Inflammation- friend or foe?
Inflammation is the immune system’s first line of defense when fighting off pathogens like bacteria and viruses and helps us heal from injury. The inflammatory response plays a crucial role in combating infection and repairing tissue damage. Without inflammation, the body couldn’t heal.
Several immune molecules play a role in inflammation, including macrophages, fibroblasts, mast cells, and dendritic cells. These molecules circulate in the blood until they pick up on invaders or cell damage to direct their response.
With all of that said, chronic activation of the inflammatory response is at the root of many diseases.
Our understanding of the connection between inflammation and disease has grown, and so have our tools to balance its response. Medicinal mushrooms are one way we can support the immune system in modulating the inflammatory response.
Types of inflammation:
- Acute inflammation: Acute inflammation is the first player to act in the immune response. A scrape on your knee that turns red and hot, a runny nose, or a fever are all the body’s natural ways of healing. We have all experienced these acute inflammatory stressors and thank our body for its effective response.
- Chronic inflammation: Chronic inflammation occurs when the immune system is constantly triggered. Instead of healing the body, the immune system creates too many pro-inflammatory molecules, like tumor necrosis factor (TNF), interleukins (ILs), prostaglandins, and free radicals – this excess causes cell damage and creates health issues.
Many factors contribute to chronic inflammation. Inflammation may be triggered by stress, foods, toxic chemicals, heavy metals, and infections. Diet plays a large role because 70-80 percent of the immune system is located in our gut. What we eat directly interacts with the immune system and can initiate an inflammatory response.
How do I know if I’m chronically inflamed?
Chronic inflammation can be hard to detect and can build up over time. Symptoms such as weight gain, fatigue, moodiness, pain, skin problems like psoriasis and eczema, allergies, and autoimmune conditions may indicate chronic inflammation.
You can also measure inflammation through blood tests. C-reactive protein (CRP) is a common inflammatory marker that can be measured in the blood. The optimal range of CRP is < 0.5 mg/L.
Homocysteine is another inflammatory amino acid linked to heart disease and other inflammatory conditions. The optimal range is <7 Umol/L.

How can I decrease inflammation?
Now that you know a bit more about optimal and chronic inflammation – what can you do?
Here is where the mushrooms step in.
Medicinal mushrooms and inflammation
Mushrooms have been used for centuries for their therapeutic effects on the body. Mushroom extracts have been used as immune modulators and for their anticancer, antibacterial, and antiviral properties. Medicinal mushrooms contain some of our most potent anti-inflammatory compounds.
Medicinal mushrooms contain active compounds that can modulate the inflammatory response. Mushrooms are rich in polysaccharides, phenolic and indolic compounds, mycosteroids, and fatty acids as well as other vitamins and biometals.
Are you ready to respond to HPV?
During chronic inflammation, the immune system is overproducing inflammatory mediators, leading to cell damage. The bioactive compounds found in mushrooms can reduce and suppress the production of inflammatory mediators through downregulating certain genes. This downregulation dampens the immune response, creating homeostasis and preventing chronic disease.
The powder of polysaccharides
Polysaccharides are one type of bioactive compound found in mushrooms. These polysaccharides inhibit inflammatory molecules including, IL-6, prostaglandins, and leukotrienes.
Glucans are one type of polysaccharide found to adjust the immune system by binding to receptors in the digestive tract and activating the immune response. The glucans stimulate the production of immune molecules such as natural killer cells, cytokines, and T helper cells. These immune molecules signal the rest of the immune system to kick into gear.
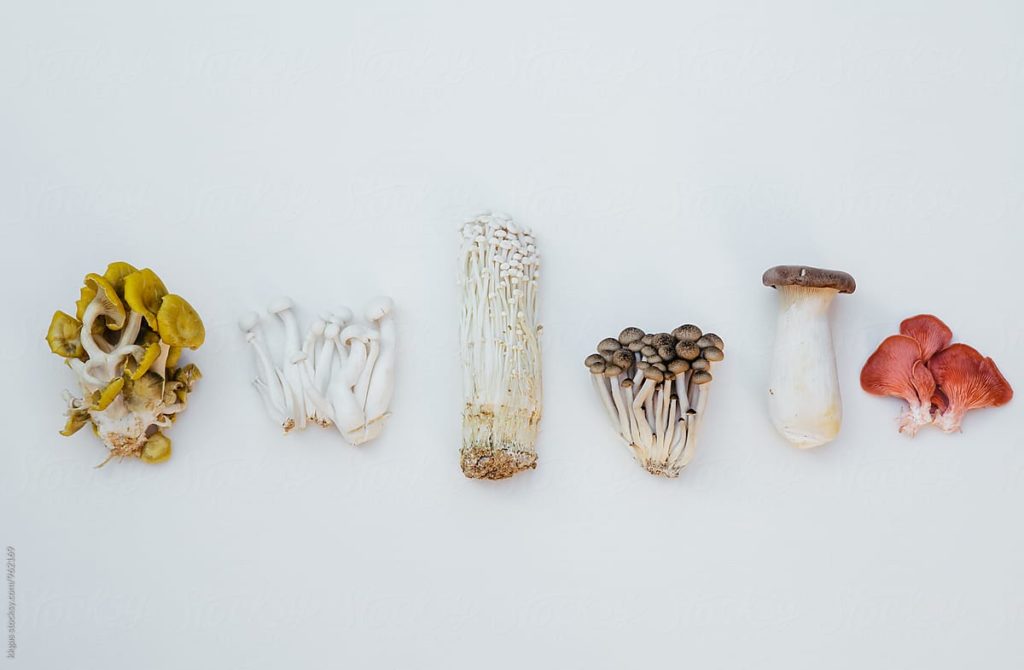

What mushrooms can help inflammation:
- Reishi: Also called the mushroom of immortality, Reishi is rich in bioactive compounds including fatty acids, polysaccharides, and peptides found to inhibit inflammation. The polysaccharides found in Reishi may inhibit cancer cell growth and have anti-inflammatory properties with melanoma and breast cancer.
- Chaga: Chaga mushrooms have also been found to have a potent anti-inflammatory effect. The mushroom has been found to have anti-inflammatory properties on mast cells and histamine responses. Histamine and mast cells are released in response to tissue damage and other inflammatory conditions and affect the microvasculature.
- AHCC: Stands for Active Hexose Correlated Compound, a mushroom extract that contains both alpha and beta-glucans that modulate the immune system. AHCC is a potent immune modulator that stimulates natural killer cells, cytokine, and macrophages. The extract has been evaluated as general immune support as well as an adjunctive in the treatment of cancers and viral infections.
Of course, supporting a healthy inflammatory response involves more than just a mushroom supplement. Diet, stress, environmental toxins, etc. also play a vital role. It is important to assess your lifestyle and make adjustments based on your specific risk factors. We recommend including a few mushrooms in your daily routine to offer extra immune support and keep you in balance.